After discovering Zeniq being promoted across multiple online forums, our Intel team took an interest and decided to investigate further. According to information available on their website, zeniq.com, Zeniq presents itself as a “Blockchain ecosystem for finance and investments.” The platform supposedly facilitates cryptocurrency exchanges and offers investment opportunities in various projects.
In their FAQ section, Zeniq mentions that those who purchase the ZENIQ “HUB 01” will have the option to mint ZENIQ Coins. The process of minting allows users to produce new ZENIQ Coins. Importantly, the earlier one acquires the ZENIQ “HUB 01,” the sooner they can begin minting, potentially resulting in the acquisition of more ZENIQ Coins. However, it’s worth noting that the minting option does not apply to the ZENIQ HUB “02.”
To participate in this project and invest in Zeniq Coins, investors are required to purchase the Zeniq Hub. As the value of the Zeniq Coin appreciates over time, investors can then choose to sell it or exchange it for other cryptocurrencies, thereby potentially making a profit from their investment.

Appriasal of Zeniq
Our comprehensive appraisal of Zeniq delves into multiple critical factors, with the foremost being the Zeniq Coin and its purported Zeniq Blockchain. As stated on their website, Zeniq claims that their native digital asset, the Zeniq Coin, operates on its own dedicated blockchain infrastructure. However, upon closer examination, our team found that the only reference available on their platform was to an ERC-20 token existing on the Ethereum blockchain, rather than any distinct Zeniq Blockchain. This discrepancy raises a fundamental question: where exactly is this elusive Zeniq Blockchain, and why is there no accessible information or codebase supporting its existence? The lack of transparency and clarity surrounding Zeniq’s core technology could potentially undermine investor confidence.
In response to the absence of a native blockchain, Zeniq’s explanation is that they have wrapped the ZENIQ coin into an ERC-20 token, allowing it to be traded on decentralized exchanges like Uniswap while awaiting its listing on other platforms. However, this explanation leaves lingering doubts about the legitimacy and viability of their blockchain claims. Without a publicly verifiable codebase or detailed technical information, there is no way to ascertain whether the Zeniq team has genuinely developed their blockchain as asserted. The absence of such foundational evidence gives rise to concerns about the long-term sustainability and reliability of the project.
Adding to the apprehension is the conspicuous absence of a whitepaper on the Zeniq website. Whitepapers serve as the backbone of any serious blockchain project, laying out crucial details about its vision, technology, use cases, and implementation strategy. A comprehensive whitepaper typically includes financial models, legal considerations, SWOT analysis, and a roadmap for project milestones. The fact that Zeniq has not provided such a crucial document raises serious red flags regarding their commitment to transparency and their willingness to disclose essential information to potential investors.
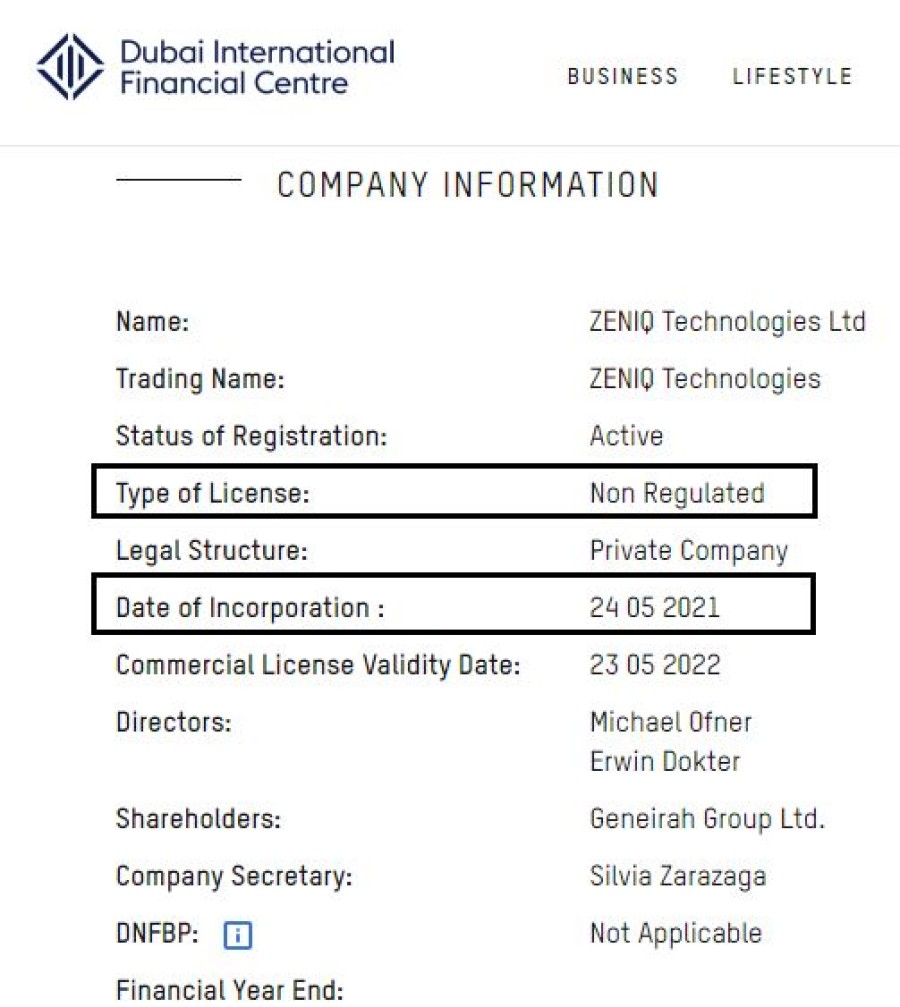
Moving beyond the technology aspect, the location and license status of the company behind Zeniq also raise significant concerns. While the Zeniq website claims the company to be a “Limited Liability Company in DIFC Freezone,” further investigation reveals two unsettling red flags on the DIFC website. The incorporation date is listed as 24th May 2021, indicating a relatively recent establishment, and the type of license is specified as “Non Regulated.” This classification suggests that the company is not authorized to provide financial services, which directly contradicts Zeniq’s claims on its website. The potential discrepancy in their business activities and license status further deepens doubts about the project’s legitimacy and credibility.

Moreover, scrutiny of Zeniq’s CEO, Erwin Dokter, yields troubling information. A search on the internet reveals his association with another crypto project called JUWELIS Digital Systems AG. Interestingly, a comparison of the FAQ section on both websites uncovers an alarming similarity in content, hinting at a possible link between the two ventures. The revelation of JUWELIS Digital Systems AG’s similar offerings and services raises questions about the originality and uniqueness of Zeniq’s value proposition. This observation, coupled with the CEO’s involvement in a previous crypto project, raises concerns about potential undisclosed connections and motives behind Zeniq’s establishment.
Considering these cumulative red flags, it is prudent for potential investors to exercise extreme caution before committing any funds to Zeniq. The absence of a whitepaper and verifiable blockchain, coupled with questions surrounding the company’s incorporation, licensing, and the CEO’s past association with another project, paint a disconcerting picture. The lack of transparency, coupled with potential indications of a rebranded project, poses significant risks and uncertainties for investors. As a result, we strongly advise individuals to conduct thorough due diligence and consider these points carefully before making any investment decisions related to Zeniq.






Add comment